When to Seek Help for Persistent Hip Pain
Hip pain is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can result from various causes, such as arthritis, tendonitis, bursitis, fractures, and infections, significantly impacting daily activities like walking, bending, and sitting. Recognizing the underlying cause and understanding available treatment options is crucial for managing hip pain effectively. Treatment typically includes physical therapy, medications, and, in some cases, surgery. Seeking medical attention is essential, particularly if the pain persists or worsens over time.
Common Causes of Hip Pain
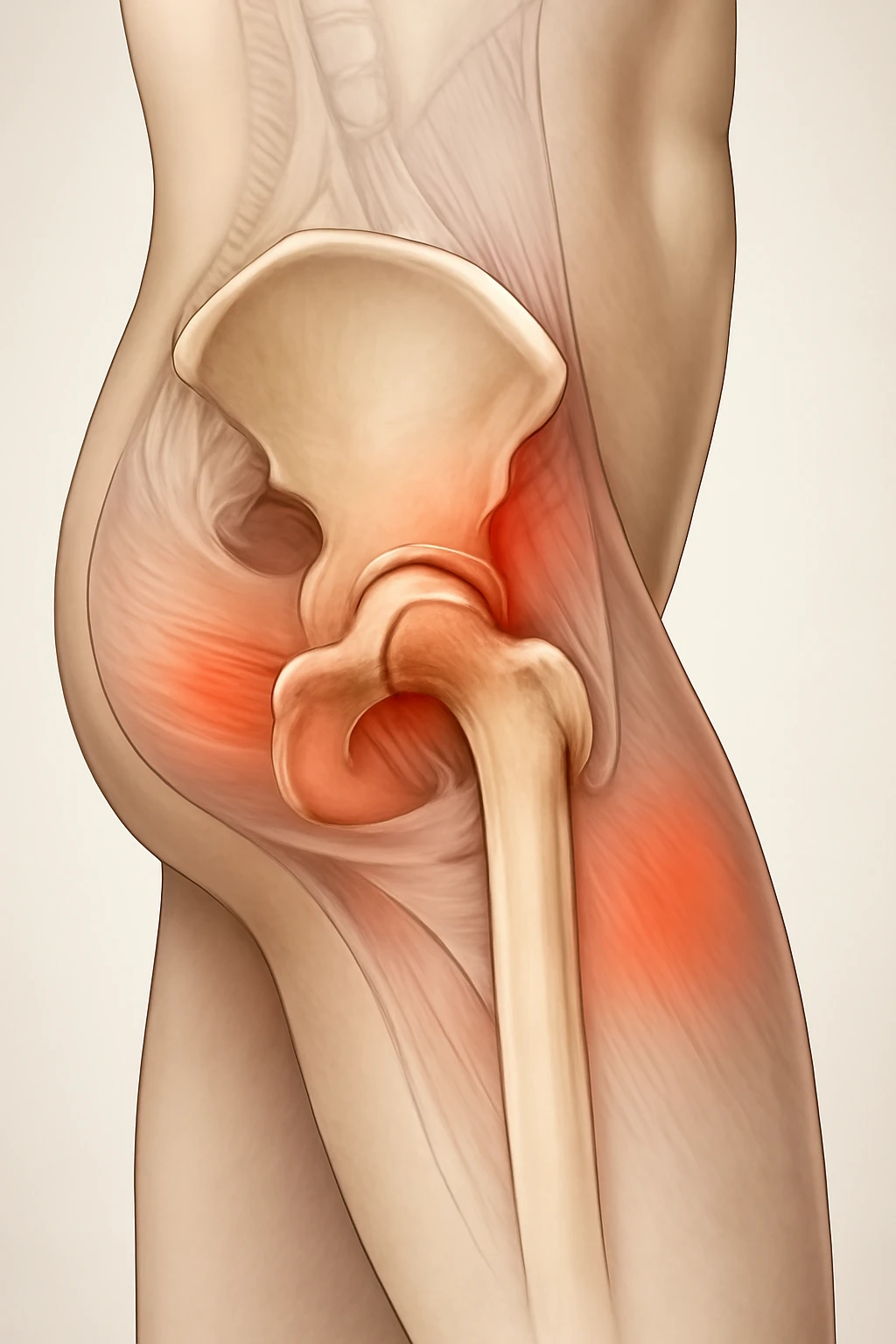
The hip joint is a crucial part of movement, and pain in this area can arise from several conditions. Common causes of hip pain include:
- Arthritis: Particularly osteoarthritis, where cartilage in the hip joint deteriorates, causing painful bone-on-bone contact, stiffness, and limited movement.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the hip joint, causing sharp pain and swelling, especially during movement.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) near the hip joint, which can cause pain when sitting or lying down.
- Fractures: Especially common in older adults or those with weakened bones, fractures can lead to sudden, intense pain, requiring immediate medical intervention.
- Infections: Though less common, infections such as septic arthritis can cause severe hip pain and may need antibiotic treatment or surgery.
These conditions can significantly limit mobility, making daily activities more challenging. Recognizing the causes of hip pain helps in seeking the right treatment and managing the condition more effectively.
Common Symptoms of Hip Pain
Hip pain can present in various ways, and its location can provide important clues to the underlying cause. Symptoms of hip pain may include:
- Groin Pain: Often associated with arthritis or tendonitis.
- Outer Thigh Pain: Can indicate muscle, ligament, or bursae issues.
- Buttocks Pain: Can result from muscle or ligament problems around the hip joint.
The pain may range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation, depending on the severity of the condition. In addition to pain, other symptoms often accompany hip problems:
- Stiffness: Common, especially after rest or in the morning, limiting the range of motion.
- Swelling: Particularly in conditions like bursitis or tendonitis.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty with activities like walking, bending, or sitting comfortably due to pain and stiffness.
If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and explore treatment options.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Hip Pain
While mild hip pain may resolve on its own, there are times when medical intervention is necessary. Recognizing warning signs early can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes. Warning signs that require medical attention include:
- Persistent or Worsening Pain: If pain continues despite home remedies, it may indicate a more serious underlying issue.
- Increasing Pain Intensity: If pain becomes more frequent or severe, seeking medical evaluation is crucial.
- Inability to Bear Weight or Move the Hip Joint: This could indicate conditions like hip fractures, severe arthritis, or infections that need immediate attention.
If you notice these symptoms, consult your healthcare provider promptly. Early intervention can significantly improve the management of hip pain and prevent further damage to the joint.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Hip Pain
Diagnosing hip pain involves physical exams and imaging tests. A healthcare provider typically starts by reviewing your medical history and asking about the symptoms, including the onset, location, and intensity of the pain. A physical examination follows, where the provider assesses the range of motion and checks for tenderness, swelling, or inflammation. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be used to get a clearer view of the hip joint’s structure and identify issues like fractures, arthritis, or soft tissue damage.
Treatment Options for Hip Pain
- Physical Therapy: Focuses on strengthening muscles around the hip joint, improving flexibility, and restoring mobility.
- Medications: NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) can help reduce pain and inflammation. For more severe cases, stronger pain relievers or corticosteroid injections may be needed.
- Surgery: If non-surgical treatments are ineffective, surgery, such as hip replacement or hip arthroscopy, may be considered to restore function and alleviate pain.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to managing hip pain and preventing further damage. If you experience persistent or worsening pain, seeking professional care is important to create an effective treatment plan.
Preventing and Managing Hip Pain
Preventing hip pain and managing chronic discomfort are essential for maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle. Incorporating exercises, posture correction, and lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of hip pain and improve the quality of life for those already affected.
Prevention Tips
- Exercise and Strengthening: Regular physical activity that targets the hip joint can reduce pain and improve stability. Focus on exercises that enhance flexibility and strength, such as swimming, walking, or hip-strengthening exercises.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight adds pressure to the hip joint, increasing the risk of conditions like arthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the hips and help prevent chronic pain.
- Posture Correction: Proper posture, particularly when sitting or standing for long periods, distributes weight evenly across the hip joint. Using ergonomic furniture can help reduce strain.
Managing Chronic Hip Pain
- Physical Therapy: Improves strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Regular therapy sessions can reduce stress on the hip joint.
- Medications: NSAIDs like ibuprofen help with pain and inflammation. For more severe pain, stronger pain relievers or corticosteroid injections may be used.
- Surgery: If conservative treatments don’t provide relief, surgical options like hip replacement or hip arthroscopy may be considered to restore function and alleviate pain.
In addition to medical treatments, coping strategies such as support groups, counseling, and stress reduction techniques can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with chronic hip pain. By adopting preventive measures and taking an active role in managing your condition, you can maintain mobility and enjoy a higher quality of life despite chronic discomfort.
Key Facts About Hip Pain
- Arthritis is a leading cause of hip pain, resulting in inflammation and reduced joint mobility.
- Tendonitis and bursitis around the hip joint can cause sharp pain, swelling, and limited movement.
- Fractures, especially in older adults, cause sudden, intense pain and may require immediate medical attention.
- Infections can cause severe hip pain and may require antibiotics or surgery for treatment.
- Physical therapy strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and is a highly effective treatment for managing hip pain.
- Medications, such as NSAIDs, help manage pain and inflammation in hip conditions.
- Surgery, including hip replacement, may be necessary for severe cases to restore function and reduce pain.
- If hip pain persists or worsens, seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hip Pain
What are the most common causes of hip pain?
The most common causes of hip pain include arthritis (especially osteoarthritis), tendonitis, bursitis, fractures, and infections. Each condition can lead to varying degrees of discomfort and mobility issues.
How do I know if my hip pain is serious?
If your hip pain persists or worsens over time, or if you’re unable to bear weight or move the joint, it’s important to seek medical attention. These could indicate a more serious condition, such as a fracture or severe arthritis.
Can physical therapy help with hip pain?
Yes, physical therapy is highly effective for managing hip pain. It focuses on strengthening the muscles around the hip joint, improving flexibility, and restoring mobility, which can reduce pain and prevent future injuries.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent hip pain?
Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the hip joint are key factors in preventing hip pain. These steps help reduce strain and improve joint health over time.
When should I consider surgery for hip pain?
Surgery, such as hip replacement or hip arthroscopy, may be recommended if non-surgical treatments like physical therapy and medications don’t provide relief. This is typically considered for severe arthritis or significant joint damage.
Can hip pain be managed without medication?
Yes, in many cases, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and alternative treatments like heat or ice therapy can help manage hip pain. Medications are usually considered when pain becomes more severe or persistent.
How long does it take to recover from hip pain?
Recovery time varies depending on the cause of the pain and the treatment. Mild conditions like tendonitis may improve in a few weeks with physical therapy, while more severe conditions, such as after surgery, can take several months.