Indigestion: Common Causes and Effective Treatments
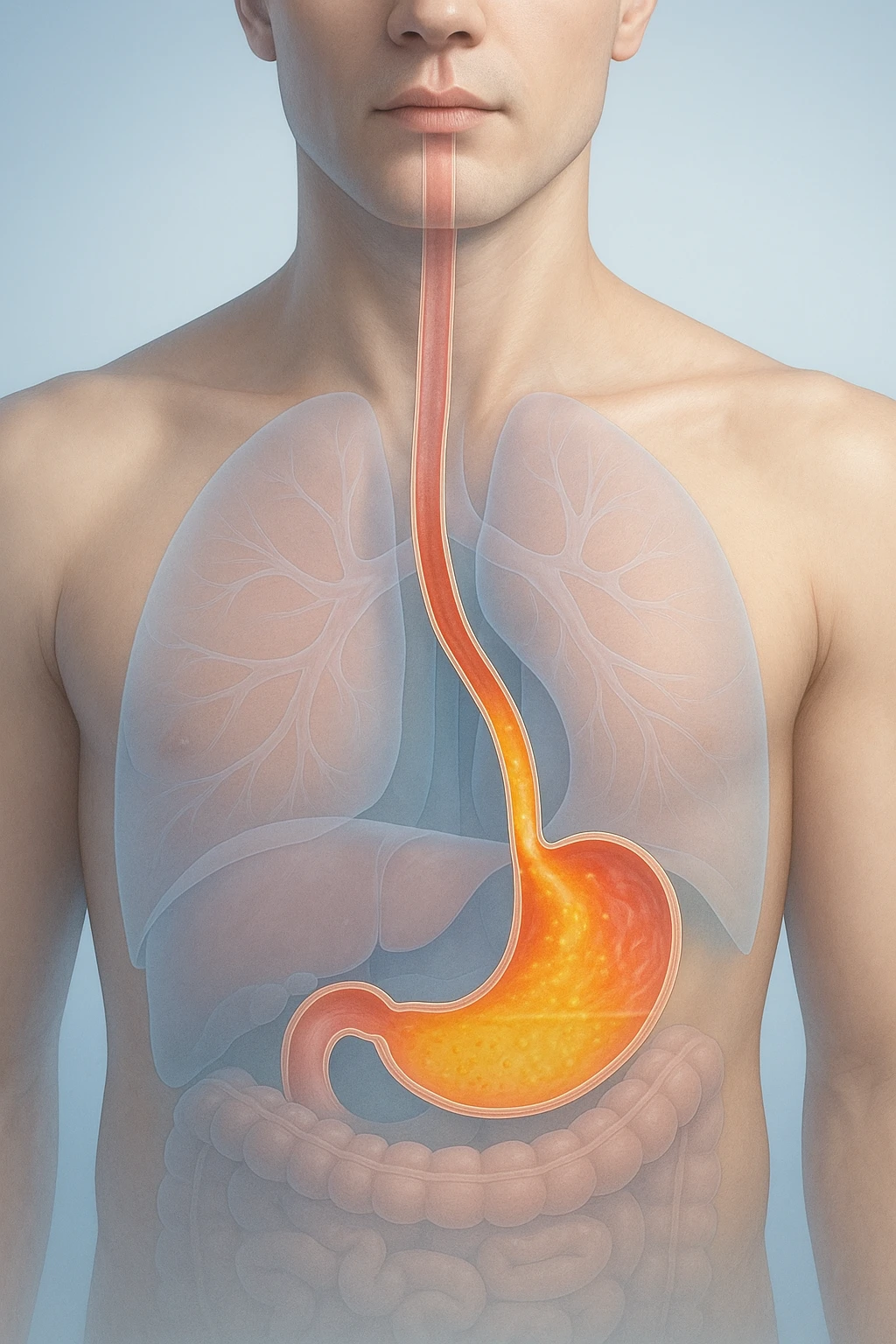
What is Indigestion?
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, refers to a group of symptoms that affect the upper digestive tract. These symptoms often include:
- Upper abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Early fullness during meals
- Nausea
The discomfort can be intermittent or chronic and may vary in severity from person to person. Indigestion can occur for a variety of reasons, but it is often linked to eating habits or underlying gastrointestinal conditions.
It is important to distinguish indigestion from related conditions like heartburn. While both can cause similar sensations in the upper abdomen, indigestion typically involves a wider range of symptoms, such as bloating and nausea, while heartburn is more specifically characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat caused by acid reflux. Understanding indigestion is crucial for effective management, as it can significantly affect quality of life and may require lifestyle modifications or medical treatment.
Indigestion Symptoms
Main Symptoms
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, is characterized by several common symptoms. These often include:
- Upper abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Early fullness during meals
- Nausea
The pain can range from mild discomfort to more severe cramping. Bloating often accompanies the pain, leading to a feeling of fullness or tightness in the stomach area. In some cases, nausea may also occur, especially after eating. These symptoms can vary in their intensity and may last for a few minutes or several hours, depending on the underlying cause and individual factors.
When to Seek Medical Help
While indigestion is generally not a cause for alarm, it is important to know when to seek medical attention. If symptoms are persistent, severe, or interfere with daily activities, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider. Particularly concerning signs include:
- Frequent or chronic abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Symptoms that do not improve with over-the-counter treatments
In some cases, indigestion can be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as acid reflux or a peptic ulcer, which requires professional evaluation and treatment.
Causes of Indigestion
Functional Dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia is a common cause of indigestion where individuals experience discomfort in the upper abdomen without an identifiable underlying disease. This condition, often referred to as ‘non-ulcer dyspepsia’, typically presents with symptoms like bloating, nausea, and early fullness after eating. The exact cause of functional dyspepsia is not well understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of factors, including altered stomach motility, increased sensitivity to stomach acid, and potential disruptions in the normal functioning of the digestive system.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Gastrointestinal disorders are another major category of causes for indigestion. Conditions such as acid reflux, gastritis, and H. pylori infections can all contribute to the development of indigestion symptoms. These conditions can be summarized as follows:
- Acid Reflux (GERD): Occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and a burning sensation.
- Gastritis: The inflammation of the stomach lining, which can result in bloating, nausea, and upper abdominal pain.
- H. pylori Infections: A bacterial infection in the stomach that causes inflammation, ulcers, and other digestive issues.
Lifestyle and Diet Factors
Lifestyle factors, such as poor diet, high stress levels, and overeating, can also contribute to indigestion. Key lifestyle factors include:
- Eating large, fatty meals or consuming caffeine, alcohol, or spicy foods
- Eating too quickly
- Chronic stress, which can exacerbate digestive problems
- Irregular eating habits, such as skipping meals or eating late at night
Diagnosing Indigestion
Medical History and Symptoms Review
The first step in diagnosing indigestion is a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. During this stage, the healthcare provider will ask about the nature and duration of the symptoms, such as:
- Upper abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Early fullness after eating
Understanding the patient’s lifestyle factors, such as dietary habits, stress levels, and any recent changes in health, can help pinpoint potential causes. The provider may also inquire about any medications being taken, as certain drugs can contribute to indigestion.
Common Diagnostic Tests
If the medical history and symptoms suggest an underlying condition that may be causing the indigestion, further diagnostic tests may be necessary. Common tests include:
- Endoscopy: A procedure that allows the doctor to visually inspect the upper digestive tract for signs of inflammation, ulcers, or other issues.
- Imaging studies: X-rays or ultrasounds to rule out other conditions.
- H. pylori testing: A test to check for H. pylori infection, a bacteria linked to peptic ulcers.
Preventing Indigestion
Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing indigestion starts with making healthy lifestyle changes. Managing stress is a crucial factor in preventing indigestion, as stress can exacerbate symptoms and affect digestion. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help reduce stress and promote better digestive health. Additionally, avoiding overeating is important. Large meals can overload the digestive system and trigger symptoms, so eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day is often beneficial. Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines can also support digestion and help prevent the discomfort associated with indigestion.
Long-term Dietary Habits
Diet plays a significant role in preventing indigestion. Adopting long-term dietary habits, such as eating balanced meals and avoiding trigger foods, can help manage and reduce symptoms. Foods and drinks that may worsen indigestion, such as fatty foods, carbonated drinks, and caffeine, should be minimized. Additionally, consuming fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can promote healthy digestion. It is also recommended to listen to your body and identify specific foods that may trigger symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dietitian is advisable for personalized dietary advice to ensure a diet that supports digestive health while avoiding common irritants.
Indigestion Treatment and Dietary Management
Medications and Medical Treatments
Treatment for indigestion largely depends on the underlying cause. If indigestion is linked to acid-related conditions, medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers may be prescribed to reduce stomach acid production. These medications help alleviate discomfort and promote healing in the digestive tract. For cases where indigestion is caused by H. pylori infections, antibiotics may be used to eradicate the bacteria and resolve symptoms. In some cases, antacids or other medications to neutralize stomach acid may also be recommended for short-term relief.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary management is crucial in controlling indigestion symptoms. Avoiding certain foods and drinks that can irritate the stomach is often recommended. These include:
- Fatty foods
- Carbonated drinks
- Caffeine
- Spicy foods
All of these can trigger or worsen indigestion. Eating smaller, more frequent meals rather than large meals can also help manage symptoms. It’s important to listen to your body and identify any specific foods that seem to worsen your symptoms, as these may vary from person to person.
Mental Health Considerations
Stress and anxiety are common contributors to indigestion. Mental health therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be beneficial in addressing the psychological aspects of indigestion. CBT helps individuals identify and manage stressors that may be exacerbating digestive symptoms. Additionally, practices such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and stress management can play a role in reducing the impact of stress on digestion.
Preventing Indigestion: Lifestyle and Dietary Approaches
Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing indigestion starts with making healthy lifestyle changes. Managing stress is a crucial factor in preventing indigestion, as stress can exacerbate symptoms and affect digestion. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help reduce stress and promote better digestive health. Additionally, avoiding overeating is important. Large meals can overload the digestive system and trigger symptoms, so eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day is often beneficial. Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines can also support digestion and help prevent the discomfort associated with indigestion.
Long-term Dietary Habits
Diet plays a significant role in preventing indigestion. Adopting long-term dietary habits, such as eating balanced meals and avoiding trigger foods, can help manage and reduce symptoms. Foods and drinks that may worsen indigestion, such as fatty foods, carbonated drinks, and caffeine, should be minimized. Additionally, consuming fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can promote healthy digestion. It is also recommended to listen to your body and identify specific foods that may trigger symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dietitian is advisable for personalized dietary advice to ensure a diet that supports digestive health while avoiding common irritants.
- Indigestion symptoms often include upper abdominal pain, bloating, fullness after meals, and nausea.
- These symptoms can vary in severity and may be intermittent or chronic.
- Indigestion can be caused by conditions like functional dyspepsia, acid reflux, and H. pylori infections.
- Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, stress, and overeating can contribute to indigestion.
- Treatment depends on the cause and may include medications like PPIs, H2 blockers, and antibiotics for H. pylori.
- Lifestyle and dietary changes, such as avoiding fatty foods, carbonated drinks, and caffeine, are commonly recommended.
- A healthy diet is key to managing indigestion. Avoid foods and drinks that worsen symptoms.
- Consult a healthcare provider or dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
- What are the main symptoms of indigestion? Indigestion typically causes upper abdominal pain, bloating, early fullness after meals, and nausea. These symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency.
- What causes indigestion? Indigestion can result from conditions like functional dyspepsia, acid reflux, and H. pylori infections. Poor diet, stress, and overeating are also contributing factors.
- When should I see a doctor about indigestion? Seek medical attention if symptoms persist, worsen, or interfere with daily life. Especially concerning signs include unexplained weight loss and symptoms that don’t improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- How is indigestion diagnosed? Doctors typically review your symptoms and medical history. Tests like endoscopy or imaging studies may be used to determine if an underlying condition, like acid reflux or ulcers, is causing the indigestion.
- Can lifestyle changes help prevent indigestion? Yes, managing stress, avoiding overeating, and eating smaller, more frequent meals can help reduce the risk of indigestion. Regular physical activity also supports digestive health.
- What role does diet play in indigestion? A healthy diet is essential. Avoiding foods and drinks that trigger symptoms, such as fatty foods, caffeine, and carbonated drinks, can help prevent or alleviate indigestion.
- Is indigestion related to heartburn? While indigestion and heartburn can both cause upper abdominal discomfort, indigestion often includes additional symptoms like bloating and nausea, whereas heartburn is characterized mainly by a burning sensation caused by acid reflux.
- What treatments are available for indigestion? Treatment varies depending on the cause but may include medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 blockers, or antibiotics for H. pylori infections. Lifestyle and dietary changes are often recommended as well.