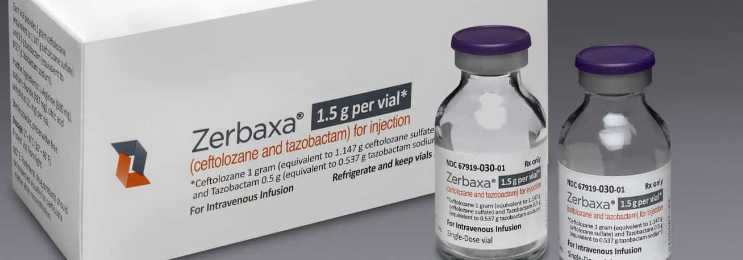
Ceftolozane/Tazobactam (Zerbaxa)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Ceftolozane/tazobactam (brand name: Zerbaxa) is a combination antibiotic used to treat serious infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria, especially when resistance to other antibiotics is suspected or confirmed. It is particularly effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including multidrug-resistant strains.
This medication is typically prescribed for:
- Complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI), in combination with metronidazole
- Complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), including pyelonephritis
- Hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia (HABP) and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (VABP)
Zerbaxa is often reserved for use when first-line treatments (such as older beta-lactams or fluoroquinolones) are ineffective due to bacterial resistance.
How should this medication be used: what is the dosage and duration?
Ceftolozane/tazobactam is administered intravenously (IV), usually in a hospital or supervised clinical setting. The dosage and treatment duration depend on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient’s kidney function.
Standard dosing for adults with normal kidney function:
- cUTI or cIAI: 1.5 g (1 g ceftolozane / 0.5 g tazobactam) every 8 hours
Treatment duration: typically 4–14 days - HABP/VABP: 3 g (2 g ceftolozane / 1 g tazobactam) every 8 hours
Treatment duration: typically 7–14 days
Renal impairment adjustment: Dosage must be reduced in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment. For patients on hemodialysis, individualized dosing is necessary.
Administration should only be performed by qualified medical personnel using sterile technique.
What should I know before taking this medication?
Ceftolozane/tazobactam is a potent antibiotic that should only be used when clearly needed. Because it is administered in a hospital setting, many risks are monitored by healthcare professionals, but patients and caregivers should still be aware of the following:
- Allergic reactions: Even if you’ve never had issues with antibiotics before, there’s still a risk of hypersensitivity. Reactions can range from mild rash to severe anaphylaxis.
- Clostridioides difficile–associated diarrhea (CDAD): Like many broad-spectrum antibiotics, ceftolozane/tazobactam can disrupt normal gut flora, leading to serious diarrhea caused by C. difficile. This may occur during or even weeks after treatment ends.
- Kidney function monitoring: Because the drug is cleared renally, impaired kidney function can lead to drug accumulation and toxicity. Blood tests may be required regularly.
- Superinfection risk: Prolonged use may allow resistant organisms or fungi (like Candida) to flourish, potentially causing secondary infections.
- Interaction with lab tests: This medication may interfere with certain urine glucose tests (e.g., Clinitest®), leading to false results.
Always inform your medical team if you develop symptoms like new rash, fever, shortness of breath, or severe diarrhea during or shortly after therapy.
What special dietary instructions should I follow?
There are no specific dietary restrictions associated with ceftolozane/tazobactam. It does not interact significantly with food, as it is administered intravenously.
However, patients may be advised to:
- Maintain adequate hydration, especially if also receiving nephrotoxic drugs
- Avoid unnecessary supplements or herbal products during IV antibiotic therapy unless cleared by a physician
- Monitor nutritional intake if gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, diarrhea) develop during treatment
For patients with abdominal infections or those recovering from surgery, a modified or restricted diet may be advised as part of overall treatment, but not because of the antibiotic itself.
What should I do if I forget a dose?
Since ceftolozane/tazobactam is administered in a clinical setting by healthcare professionals, missed doses are rare. The timing and dosing are carefully managed by the medical team, especially for serious infections.
However, in outpatient or home infusion scenarios (e.g., long-term IV therapy managed by visiting nurses or home infusion services), the following applies:
- If a dose is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible.
- If it is almost time for the next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose—do not double up.
- Always follow your doctor or pharmacist’s instructions regarding how to manage missed doses.
Any interruption in antibiotic therapy, especially for resistant infections, should be reported to the prescribing physician immediately. Delayed or inconsistent dosing can reduce the drug’s effectiveness and promote bacterial resistance.
What side effects can this medication cause?
Like all antibiotics, ceftolozane/tazobactam may cause side effects. Most are mild and resolve after therapy ends, but some can be serious and require medical attention.
Common side effects include:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Pyrexia (fever)
- Elevated liver enzymes (asymptomatic)
Serious side effects (seek medical attention):
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling, shortness of breath, anaphylaxis)
- Clostridioides difficile–associated diarrhea (persistent or bloody diarrhea)
- Kidney dysfunction (reduced urine output, elevated creatinine)
- Seizures (rare, more likely in patients with renal impairment or CNS disorders)
All side effects should be monitored closely in hospitalized patients. In outpatient settings, any new or concerning symptoms should prompt an immediate call to a healthcare provider.
Use in children, pregnant people, and older adults
Children:
As of the most recent FDA updates, ceftolozane/tazobactam is approved for pediatric use in patients aged 3 months and older for the same indications as in adults (e.g., cIAI, cUTI, HABP/VABP), with appropriate weight-based dosing. Clinical trials have demonstrated a safety profile similar to that observed in adults. Dosing and administration must be handled by experienced pediatric infectious disease specialists.
Pregnancy:
Ceftolozane/tazobactam is classified as Pregnancy Category B. Animal studies have not shown harm to the fetus, but there are no well-controlled studies in pregnant humans. It should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed, and the potential benefits outweigh the risks. As with all antibiotics, use in pregnant women requires individualized risk assessment.
Breastfeeding:
It is not known whether ceftolozane or tazobactam is excreted in human milk. Because many beta-lactams are present in breast milk in small amounts, caution is advised. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, depending on the importance of the therapy to the mother.
Older adults (65+):
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients. However, older patients are more likely to have impaired renal function, which may necessitate dosage adjustment and more frequent monitoring of kidney parameters during treatment.
Use in people with other medical conditions
Ceftolozane/tazobactam must be used with caution in patients who have co-existing medical conditions, as these can affect how the drug is metabolized, tolerated, or cleared from the body.
Renal impairment:
This is the most critical consideration. Since both components are primarily excreted via the kidneys, patients with reduced renal function are at high risk for drug accumulation and toxicity.
- Dose adjustments are mandatory for patients with moderate, severe, or end-stage renal disease (including those on dialysis).
- Close monitoring of creatinine levels and urine output is essential during therapy.
Hepatic impairment:
While ceftolozane/tazobactam is not metabolized by the liver, liver enzyme elevations have been observed in some patients. Use cautiously in those with severe liver disease, and monitor liver function tests periodically.
Neurological disorders:
There have been rare reports of seizures and altered mental status, especially in patients with renal dysfunction. Patients with pre-existing seizure disorders or CNS abnormalities should be monitored closely.
Immunocompromised patients:
Zerbaxa may be used in neutropenic or immunosuppressed patients (e.g., those with cancer or post-transplant), particularly in cases of resistant Gram-negative infections. However, due to increased risk of superinfection and slower response, careful microbiological and clinical monitoring is essential.
Use of this medication and the ability to drive or operate machinery
Ceftolozane/tazobactam does not directly impair cognition, coordination, or reaction time in most individuals. It is not classified as a central nervous system depressant and does not typically cause drowsiness or dizziness.
However, there are situations in which driving or operating heavy machinery may not be advisable:
- If you are experiencing side effects such as headache, fatigue, dizziness, or confusion
- If you have underlying renal impairment, which can increase the risk of neurotoxic effects (e.g., seizures, encephalopathy)
- If the medication is part of a broader inpatient treatment plan that includes sedating drugs or CNS-active agents
Patients recovering from severe infections or still undergoing intravenous therapy (especially at home) should avoid operating vehicles or machinery unless explicitly cleared by their physician.
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?
Ceftolozane/tazobactam is supplied as a powder for intravenous infusion and must be reconstituted and diluted prior to administration. Storage and disposal are typically handled by hospital pharmacies or trained outpatient infusion services.
For unopened vials:
- Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F)
- Protect from light
- Do not freeze
Once reconstituted:
- The solution must be used within a specific time frame (usually within 24 hours refrigerated or 1 hour at room temperature), depending on the diluent and storage conditions.
- Always follow specific handling instructions provided with the drug.
Disposal:
- Do not flush unused portions or IV bags down the drain.
- Use a medication take-back program or return to the hospital/pharmacy for safe disposal.
- If self-administered at home, follow the waste protocols from your home health provider.
In case of emergency/overdose
Ceftolozane/tazobactam overdose is rare, especially in hospital settings where dosing is strictly monitored. However, overdose can occur, particularly in patients with undetected or worsening renal impairment, leading to drug accumulation.
If an overdose is suspected—either due to dosing error, incorrect renal adjustment, or accidental re-administration—seek emergency medical help immediately.
In medical settings, management may include:
- Discontinuation of the drug
- Symptomatic treatment and supportive care
- Hemodialysis to help remove the drug, as both components are dialyzable to some extent
Symptoms of overdose
Most symptoms of overdose reflect amplified side effects, especially those related to the nervous system and kidneys.
Potential symptoms include:
- Nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal distress
- Altered mental status: confusion, agitation, hallucinations
- Seizures (particularly in those with impaired renal function)
- Muscle twitching or tremors
- Reduced urine output or signs of acute kidney injury
- Severe allergic reactions, though uncommon in overdose scenarios
Any of these signs require immediate clinical attention. Patients undergoing outpatient infusions or with at-home IV access should have emergency contact instructions readily available.
What other information should I know?
- Ceftolozane/tazobactam is not effective against all types of bacteria. It works primarily on aerobic Gram-negative organisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It has limited or no activity against Gram-positive cocci (except in combination with other drugs), anaerobes, or atypical pathogens. Always use culture and sensitivity testing to guide its appropriateness.
- Antibiotic stewardship is critical. Zerbaxa is part of the “reserved antibiotics” group. Inappropriate use increases the risk of resistance development, making future infections harder to treat.
- It should not be used to treat viral infections, such as the common cold, flu, or COVID-19. Like all antibiotics, using it without bacterial confirmation is strongly discouraged.
- Inform all healthcare providers you are receiving or have recently received this antibiotic—especially if you require other IV medications, undergo surgery, or experience new symptoms after hospital discharge.
- Medical alert: If you are receiving long-term therapy or are prone to allergic reactions, consider wearing a medical ID that includes information about ceftolozane/tazobactam use.
Brand names
- Zerbaxa (marketed by Merck & Co.)
This is currently the only FDA-approved brand combining ceftolozane and tazobactam.
Combination product brand names
Ceftolozane/tazobactam itself is a fixed-dose combination product and not marketed under other brand combinations. However, it may be co-administered with other drugs (e.g., metronidazole for intra-abdominal infections), and these regimens may appear under protocol-based hospital treatment names.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Zerbaxa used for, and how is it different from regular antibiotics?
Zerbaxa is a strong antibiotic used for serious infections, especially when bacteria are resistant to standard drugs. It’s not for simple infections like strep throat or earaches — it’s usually used in hospitals for people with complicated urinary, abdominal, or lung infections.
Why can’t I just take this antibiotic at home as pills?
Zerbaxa is given only by intravenous (IV) infusion because it doesn’t work properly when taken by mouth. The drug needs to reach high levels in the blood to be effective against serious infections, which is why it’s typically used in hospital settings.
Is this medication safe for people with kidney problems?
It can be, but the dose must be carefully adjusted. If your kidneys don’t work well, the drug can build up in your body and cause side effects, including confusion or seizures. Your medical team will usually monitor your kidney function closely during treatment.
Can Zerbaxa treat COVID-19, flu, or other viruses?
No. Zerbaxa only works against bacteria. It won’t help with viral infections like COVID-19, influenza, or the common cold. Using antibiotics for viral illnesses can do more harm than good, including causing resistance.
What happens if I miss a dose while getting treated at home?
Call your healthcare provider or home infusion nurse immediately. Skipping or delaying doses — even by a few hours — can reduce the drug’s effectiveness and make it easier for bacteria to survive and become resistant.
I developed diarrhea during treatment — should I be worried?
If the diarrhea is mild, it may go away on its own. But if it’s severe, bloody, or continues for more than 2–3 days, it could be a sign of C. difficile infection, which needs urgent treatment. Don’t ignore it — contact your doctor.
Is it safe to drive while receiving Zerbaxa?
Most people can drive safely, but if you feel dizzy, weak, or confused, you shouldn’t drive. These side effects are rare but possible, especially if your kidney function is reduced or if you’re on other medications that affect your nervous system.
Can I breastfeed while receiving this medication?
There’s limited data, but small amounts of the drug might pass into breast milk. Discuss it with your doctor — in some cases, they may advise temporarily stopping breastfeeding while you’re receiving treatment.
Will I need other antibiotics along with Zerbaxa?
Sometimes, yes. For abdominal infections, Zerbaxa is often combined with metronidazole to cover a wider range of bacteria. Your doctor will decide the best combination based on your infection and lab results.
Do I need to finish the full course even if I feel better?
Absolutely. Stopping early can allow the infection to come back or become resistant. Always complete the full prescribed course — even if your symptoms are gone.